What are HGH boosters?
As explained above, HGH boosters are special dietary supplements that stimulate the production of human growth hormone in the body. In principle, they are comparable to testosterone boosters. Unlike testosterone boosters, however, HGH boosters are not primarily composed of plant substances. Instead, they contain synthetically produced growth hormone secretagogues (see below: How do HGH boosters work?).
What is growth hormone used for?
Growth hormone is a polypeptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that plays a central role in cell growth and metabolism. Alternative names include "somatropin" or "somatotropin," and the abbreviations STH (for "somatotropic hormone") and HGH (for "human growth hormone"). The human body produces growth hormone throughout life; however, production declines sharply after puberty.
In the first half of life, growth hormone primarily causes the body to grow taller (hence the name "growth hormone"). Later, when bone growth has ceased, it serves only to regulate body composition. Specifically, growth hormone has the following functions in adults [1]:
- Stimulation of protein synthesis (= growth of muscles and soft tissue)
- Calcium deposition (= growth/stabilization of bones and cartilage)
- Lipolysis (= fat breakdown to provide energy)
- Regulation of blood sugar levels (= stimulation of insulin secretion and subsequent reduction of blood sugar levels)
- Hydration (= storage of tissue water)
- Support of the immune system (= stimulation of T lymphocytes and macrophages)
- General cell proliferation
HGH for muscle building / HGH for fat loss
In bodybuilding, HGH is interesting in that it promotes muscle growth while simultaneously accelerating fat loss. It does exactly what bodybuilders (and male and female bodybuilders) want! It also promotes collagen formation, which makes tendons, ligaments, and joints more stable. It's no wonder, then, that the administration of external growth hormone has become established as a performance-enhancing measure in bodybuilding.
HGH doping – expensive and risky
As already mentioned, HGH is still released in adulthood, but to a much lesser extent than in childhood. The body releases the largest amounts during sleep. (Sufficient sleep is therefore one of the most effective natural "muscle builders.") Other triggers for the release of growth hormone include:
- Hypoglycemia or hunger,
- the release of certain neurotransmitters such as dopamine and
- a high concentration of thyroid hormone.
However, if you want to achieve supernatural HGH levels as an adult, neither plenty of sleep nor long periods of fasting will help. You have to resort to "more drastic" measures. For example, you can inject yourself with external HGH.
Towards the end of the 1980s, HGH injections entered professional bodybuilding. Initially, the growth hormone was extracted from the pituitary glands of corpses. This was not only gruesome, but also carried the risk of infection with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (a variant of mad cow disease). Starting in the 1990s, however, HGH could be produced recombinantly, i.e., artificially using genetically modified microorganisms, which made HGH doping extremely popular. For decades, the administration of HGH could not be detected in doping tests. It wasn't until 2010 that HGH abuse was fully analyzed [2].
However, doping with external HGH has several disadvantages.
- Pure HGH doesn't produce significant muscle growth because the hormone merely stimulates the liver to produce and release somatomedins (insulin-like growth factors [IGF1]). IGF1, in turn, requires a specific hormonal environment to initiate muscle growth. In concrete terms, this means that HGH only works as a muscle-building agent in combination with insulin and testosterone or another anabolic steroid.
- HGH from controlled laboratory production is very expensive. Since HGH treatment for muscle building must be continued over several weeks, a growth hormone "cycle" can easily cost €10,000 or more. An alternative is HGH from underground laboratories – however, you never know what the product actually contains. While underground HGH is somewhat cheaper than lab-produced HGH, due to the generally high price, growth hormone is counterfeited far more often than anabolic steroids.
- HGH must be injected. The problem is that it sometimes acts locally, so "dimples" can form at the injection site (abdomen, leg, buttocks, etc.) due to the loss of fatty tissue.
- Incorrect dosage can lead to serious side effects.
Growth hormone side effects
Side effects that may occur with the administration of external somatropin include
- Water accumulation in the tissue and a correspondingly puffy appearance, especially in the face,
- Sensory disturbances when nerves are compressed by the accumulation of water (carpal tunnel syndrome),
- a latently high blood sugar level and consequently insulin resistance or diabetes,
- a pathological enlargement of the internal organs,
- elevated liver values and
- subsequent growth of cartilage and bone ends (acromegaly), resulting in enlarged feet, hands and jaw bones.
The risk of acromegaly, in particular, deters many bodybuilders from using HGH doping. The pathological enlargement of internal organs also scares bodybuilders. However, this side effect is not nearly as severe as is often claimed. The so-called "wax belly," or bloated stomach, which can be seen in quite a few bodybuilding professionals on competition stages (also known as "bubble gut"), is actually not primarily caused by growth hormone abuse. Rather, the phenomenon is due to impaired digestion and the formation of gases that occur during carbohydrate "loading" in the pre-contest phase.
The bottom line is that the use of injectable HGH as a doping agent is not recommended for non-professionals, and certainly not for purely amateur bodybuilders without competitive ambitions. HGH boosters are a better alternative.
How do HGH boosters work?
HGH boosters essentially contain one of the following two substances (or both):
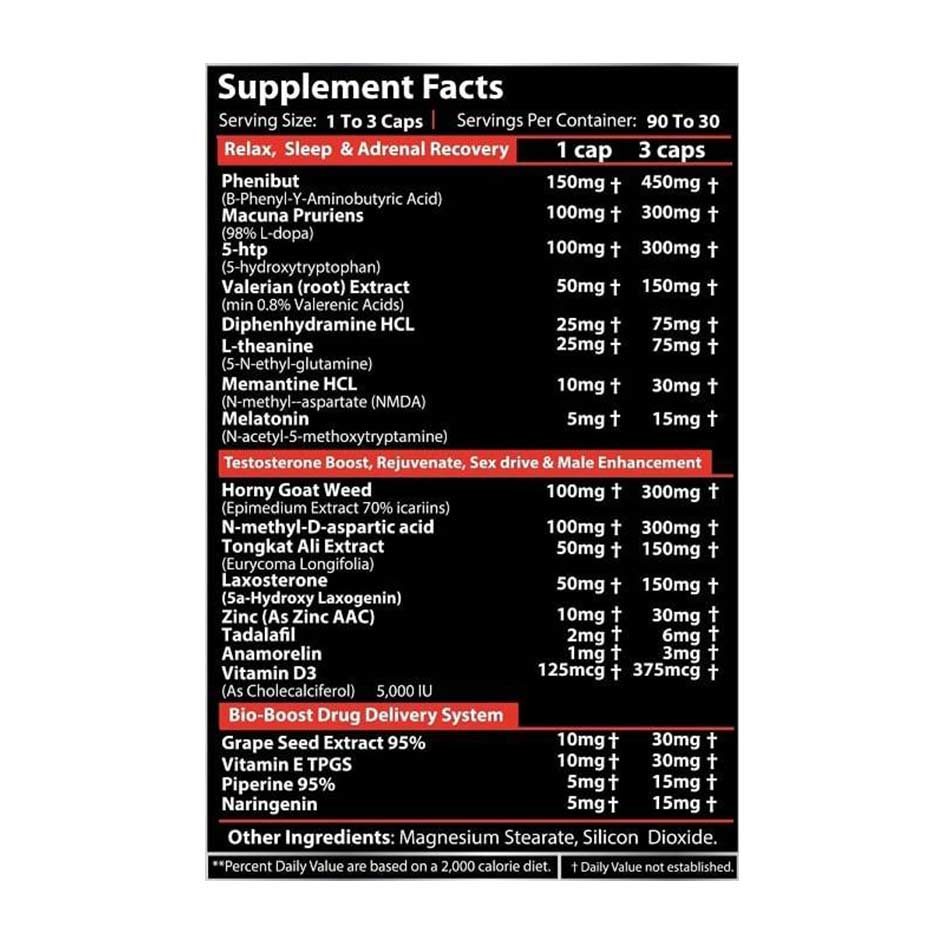
- Anamorelin
- Ibutamoren (MK-677)
These substances are growth hormone secretagogues, meaning they stimulate the pituitary gland to secrete growth hormone.
Anamorelin
Anamorelin is an orally available ghrelin mimetic, mimicking the effects of the "hunger hormone" ghrelin. Thus, it not only causes the release of growth hormone but also stimulates appetite [3]. It was developed by Helsinn Healthcare SA for the treatment of cancer cachexia and anorexia [4]. Anamorelin significantly increases plasma levels of growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) in humans. Furthermore, it increases lean body mass and muscle strength.
Ibutamoren
Ibutamoren, also called "MK-677" and "Nutrabol," is the more well-known growth hormone secretagogue compared to Anamorelin. It works similarly to Anamorelin, meaning it also functions as a ghrelin receptor agonist. MK-677 was developed by Merck & Co. and is often referred to asSARMs(Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators). In fact, Ibutamoren is not a SARM—because it acts not on the androgen receptor, but on the ghrelin receptor. Just like Anamorelin, Ibutamoren causes increased growth hormone secretion with all the associated benefits (increased bone density, increased muscle mass, reduction of body fat, etc.) [5]
Ibutamoren side effects, Anamorelin side effects
What side effects do HGH boosters have? They are certainly not the same as pure HGH – because neither Ibutamoren (MK-677) nor Anamorelin can stimulate growth hormone secretion so strongly that the body produces HGH levels similar to those seen with HGH doping. Therefore, cartilage proliferation and organ growth are not an issue with HGH boosters. Side effects that CAN occur are
- possible water retention (face, hands, feet),
- slightly elevated blood pressure (due to water retention),
- increased blood sugar levels and
- Daytime fatigue.
Water retention can be effectively counteracted by reducing salt intake and drinking diuretic tea (e.g., nettle tea). However, it will disappear anyway once you stop taking HGH boosters. What will definitely occur when using HGH boosters, however, is increased appetite. If that suits you because you're already in the bulking phase, you should take HGH boosters in the morning (once a day). If you're currently dieting—HGH boosters help with fat loss—it's better to take them before bed. After all, you're not hungry while you sleep.
Buy HGH Booster MK-677 – what should you consider?
If you want to buy an HGH booster, you first have a choice: Do you want a combination product or do you want to buy MK-677 (as an isolated product)? There are offers for both online. Anamorelin, on the other hand, is not available as a standalone product, not even as a prescription drug. This is because the European Medicines Agency has not yet granted the active ingredient approval.
Combination preparations such asG-Tropin from EX4EXhave the advantage that they contain not only Ibutamoren (MK-677) and Anamorelin but also several other useful substances, for exampleLiver protectantsHowTUDCAorN-Acetyl-L-Cysteine. (Practically allMuscle picture preparationsplace a certain strain on the liver, so a liver protectant can't hurt when using an HGH booster.) Their disadvantage is that they specify fixed dosage combinations with each capsule (e.g. 20 mg Anamorelin plus 10 mg Ibutamoren). For individual preparations such asMK677 from Sarma-ComHowever, you can determine the dosage of the individual active ingredients yourself.
But no matter what you prefer, you've come to the right place at GETBOOST3D.com! We offer premium-quality HGH boosters. We also offer:
- Transparency – with us you always know exactly what you are buying because we categorize everything correctly.
- Fast delivery – your purchased supplements will arrive at your home in a flash.
- Trustworthiness – top ratings and satisfied customers speak for themselves.
- netdoktor.de (2024): Growth hormone (https://www.netdoktor.de/anatomie/wachstumshormon/)
- pharmazeutische-zeitung.de (2020): Fraud with Somatotropin proven (https://www.pharmazeutische-zeitung.de/ausgabe-082010/betrug-mitsomatotropin-nachgewiesen/)
- sciencedirect.com (2021): Anamorelin (https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/anamorelin)
- wikipedia (2023): Anamorelin (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anamorelin)
- R. Nass et al. (2008): “Effects of an oral ghrelin mimetic on body composition and clinical outcomes in healthy older adults: a randomized trial”
(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18981485/)