What is NAC?
NAC, short for "N-acetyl-L-cysteine," is a special form of the amino acid cysteine. Cysteine is one of the so-called semi-essential amino acids and is a fundamental building block of the body's fibrous proteins. (Fibrous proteins are proteins responsible for the formation of hair, nails, bones, and cartilage.) Cysteine promotes the body's own detoxification and protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. The amino acid is found in many foods—such as poultry, eggs, and garlic—but only in small amounts.
It has been known since the 1960s that the acetyl form of cysteine, N-acetyl-L-cysteine, has expectorant properties. N-acetyl-L-cysteine is therefore still sold today as a mucolytic (expectorant). Common product names for such agents are "ACC" and "acetylcysteine." However, for NAC to have an expectorant effect, it must be administered in highly concentrated form.
What is NAC used for?
The list of positive effects of N-acetyl-L-cysteine is quite long. It's no wonder that NAC is used as a dietary supplement for various purposes. In addition to its use as an expectorant for respiratory diseases, the following uses are established (although
not all of them are based on scientifically proven findings):
- Use as an antioxidant
As already mentioned, NAC is a powerful antioxidant. This means that, due to its chemical structure, NAC has the ability (like all antioxidants) to neutralize aggressive oxygen compounds. Thus, NAC contributes to protecting cells from oxidative damage. - Use to strengthen the immune system
When NAC is ingested orally, it is subsequently converted to cysteine in the liver, and cysteine plays an essential role in the production of glutathione. (Glutathione is one of the most important cytoprotective compounds; among other things, it ensures that red blood cells can fulfill their function as oxygen transporters [1]). Studies suggest that NAC has an immune-boosting effect in glutathione-deficiency diseases such as AIDS [2]. - Use to support the liver
Since the liver is the central detoxification organ, it benefits particularly greatly from high glutathione levels. In cases of paracetamol poisoning, NAC is even used as an antidote to prevent liver cell damage [3]. This is also the reason why NAC is so popular in bodybuilding as a cycle support supplement: NAC helps the liver cope with the stress of the steroid molecules during an anabolic steroid cycle. - Use as an antidepressant
NAC also has the ability to regulate the level of the neurotransmitter glutamate in the body. In this respect, NAC can
Prevent diseases. Studies suggest that an excess of glutamate is associated with neuronal diseases such as obsessive-compulsive behavior.
bipolar disorders and schizophrenia [4]. - Use as a nootropic
Since excess glutamate is also detrimental to memory and learning performance, it stands to reason that NAC, in its function as a glutamate regulator, may also promote mental performance. However, this has not yet been confirmed by studies. - Use as a performance-enhancing substance in sports
In fact, NAC can also be used to enhance physical performance—this is demonstrated by numerous athletes' experiences with NAC. There's even a medical study that demonstrates the performance-enhancing effect of NAC: In this study, cyclists were given an intravenous NAC solution, which significantly delayed the onset of muscle fatigue. The use of NAC for performance enhancement is completely legal; N-acetyl-L-cysteine is not on the WADA list of prohibited substances.
What NAC dosage is appropriate?
The bioavailability of NAC is rather low, which is why NAC supplements should be taken in higher doses.
- For the treatment of respiratory diseasesabout 600 mg daily are recommended, as stated in the package leaflet for “ACC akut 600 mg”
(effervescent tablets). It is important to drink sufficient fluids while taking NAC – only then can it have an expectorant effect. - To strengthen the immune systemFor detoxification, the recommended daily doses range from 1,500 to 2,500 mg. If NAC is used in bodybuilding as a cycle support supplement, the higher dose (2,500 mg) should be the guideline.
- To promote concentration and motivation1,000 mg daily is sufficient, ideally divided into two portions of 500 mg each.
What are the side effects of NAC?
At the dosages mentioned above, NAC is considered safe. Little is known about NAC side effects – only gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea, abdominal pain, or diarrhea can occur occasionally. To minimize the risk of such NAC side effects, it is recommended to take it between meals. For long-term use, parallel supplementation with vitamin C is recommended (e.g., withVitamin C Powder (200 g) from Everbuild Nutrition) to prevent the formation of cystine stones.
Where can you buy NAC?
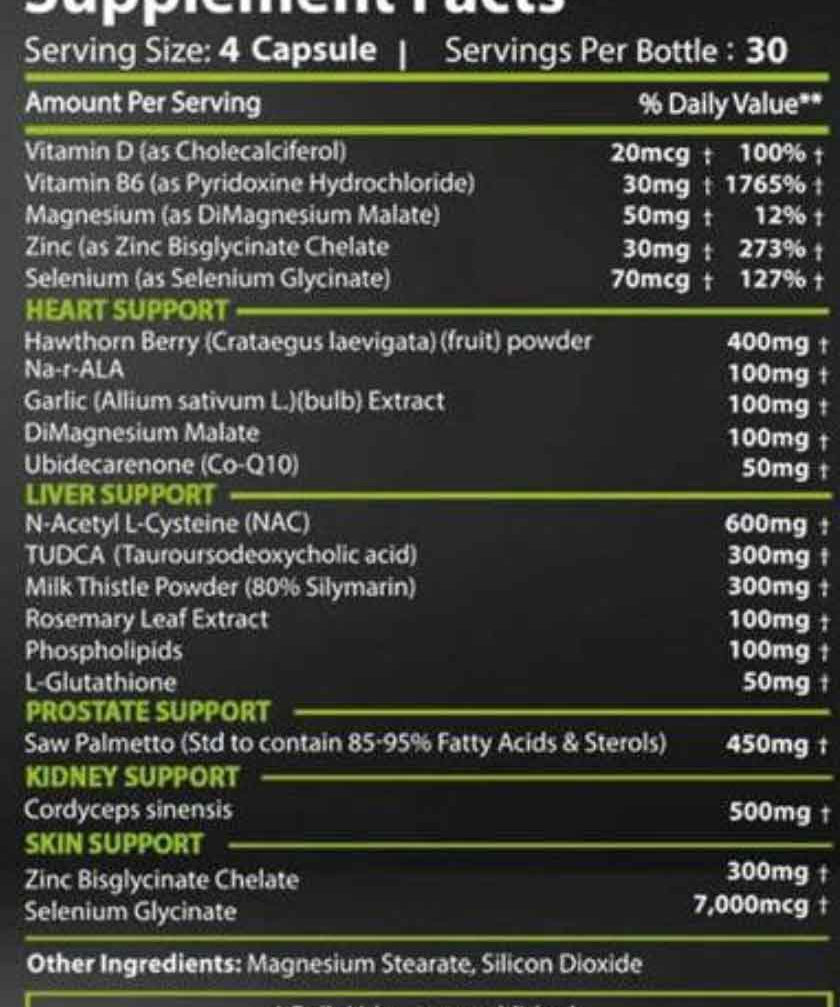
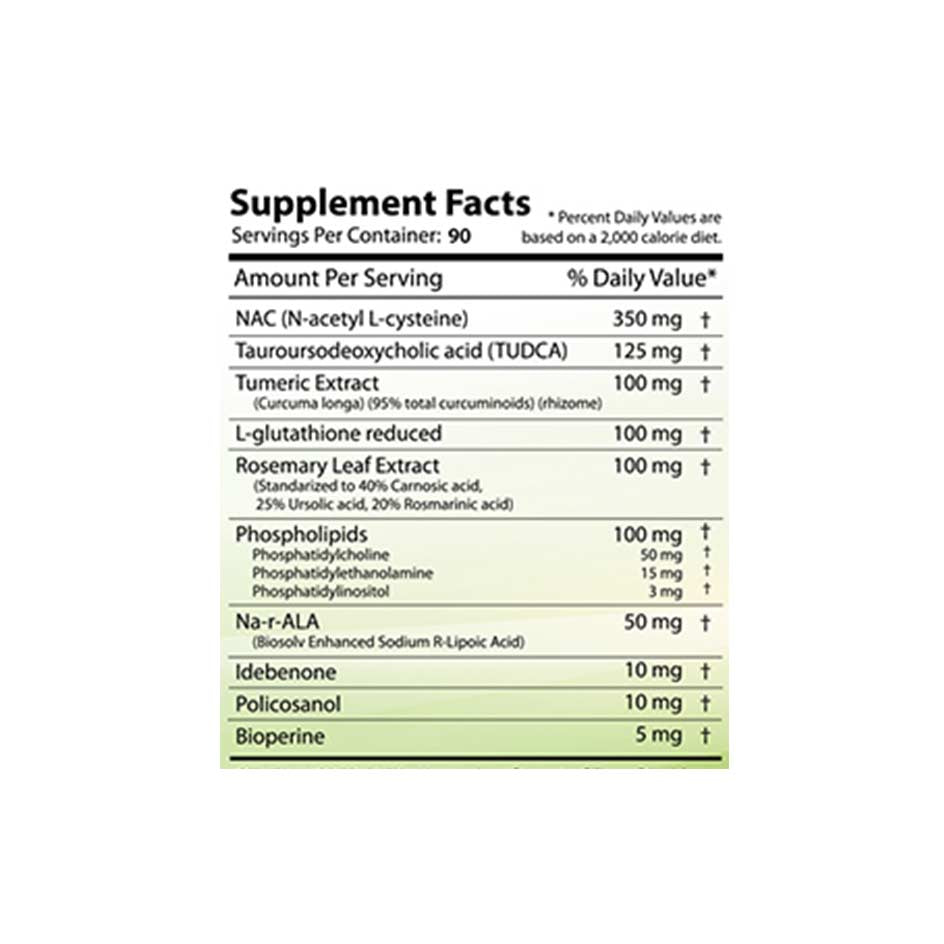
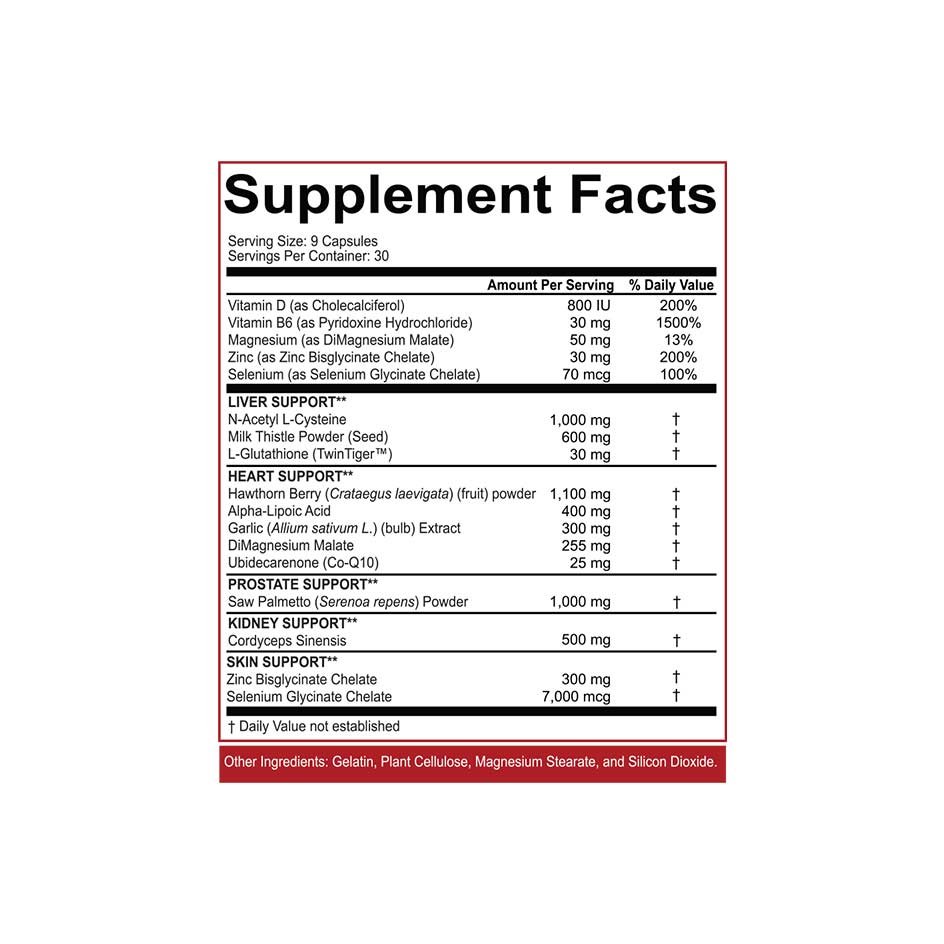
Anyone interested in purchasing NAC can do so either at a pharmacy or in an online sports supplement store. It's important to note that pharmacies often only offer NAC effervescent tablets or aerosol sprays, while online stores also offer NAC powder and capsules. Here at GETBOOST3D, we offer a wide selection of NAC supplements—both in powder form (e.g., in capsule form) and in capsule form (e.g., in capsule form).NAC 250 g from Revange Nutrition) and in capsule form (NAC 90 Capsules from Krause HoforNAC from Pure Labs). We also offer numerousCycle support supplementsthat contain NAC as an ingredient (e.g.On Cycle 120 Caps by Core Labs).
- flexikon.doccheck.com (2024): Glutathione (https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Glutathion)
- KR Atkuri (2007): “N-Acetylcysteine – a safe antidote for cysteine/glutathione deficiency” (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17602868/)
- pharmazeutische-zeitung.de (2010): N-Acetylcysteine: New findings on a proven active ingredient (https://www.pharmazeutischezeitung.de/ausgabe-402010/neue-erkenntnisse-zu-einem-bewaehrten-wirkstoff/)
- Fernandes et al. (2016): “N-Acetylcysteine in depressive symptoms and functionality: a systematic review and meta-analysis”
(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27137430/)